High frequency transformer knowledge popularization
In modern electronic devices, high-frequency transformers play a crucial role. They are not only used for energy conversion, but also play an important role in signal transmission, amplification, and isolation. This article will provide you with a detailed introduction to the principles, structures, characteristics, applications, and maintenance of high-frequency transformers.
1、 The principle of high-frequency transformer
High frequency transformer is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert electrical energy. When alternating current passes through a primary winding, an alternating magnetic field is generated. When this magnetic field passes through a secondary winding, an induced electromotive force is generated in the secondary winding, thereby achieving the transmission and conversion of electrical energy. Due to the high operating frequency of high-frequency transformers, the design of their magnetic circuits, circuits, and windings must consider high-frequency effects to ensure their normal operation.
2、 Structure of high-frequency transformer
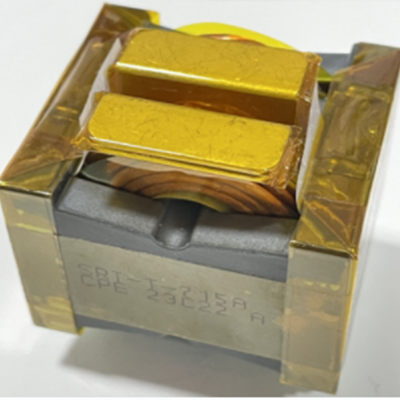
The structure of a high-frequency transformer mainly includes the iron core, winding, insulation material, and other parts.
Iron core: It is the magnetic circuit part of the transformer, usually made of high-frequency and low loss ferrite material to improve the efficiency of the transformer.
Winding: It is the circuit part of a transformer, usually made by winding high-frequency insulated wires to reduce energy loss.
Insulation material: used to isolate windings and iron cores, preventing electrical short circuits and insulation breakdown.
3、 Characteristics of high-frequency transformers
Miniaturization: The high operating frequency of high-frequency transformers makes their magnetic circuit, circuitry, and winding designs more compact, thereby achieving miniaturization of transformers.
High efficiency: High frequency transformers use ferrite materials and insulated wires with high frequency and low loss, resulting in lower losses and higher efficiency.
Low loss: During operation, high-frequency transformers have optimized the design of their magnetic circuit, circuitry, and windings, resulting in minimal iron and copper losses, thereby reducing the overall circuit losses.
High reliability: High frequency transformers use high-quality materials and advanced production processes, making them highly reliable and stable.
4、 Application of High Frequency Transformers
High frequency transformers are widely used in various electronic devices, including but not limited to:
Electronic devices: High frequency transformers are commonly used in circuits such as switching power supplies and inverters to achieve the conversion and transmission of electrical energy.
Communication equipment: High frequency transformers are commonly used in circuits such as high-frequency amplifiers and oscillators to process and transmit signals.
Medical equipment: High frequency transformers are commonly used in high-frequency therapy devices, high-frequency surgical knives, and other equipment to improve medical effectiveness.
5、 Types and Selection of High Frequency Transformers
There are various types of high-frequency transformers to choose from according to different application requirements, such as hollow coil transformers, thin film transformers, and PCB transformers. When choosing a high-frequency transformer, the following factors need to be considered:
Rated power: The rated power of a transformer is determined based on actual needs, usually measured in watts (W).
Frequency range: The frequency range of high-frequency transformers is usually from tens of kilohertz to hundreds of kilohertz, and the appropriate frequency range needs to be selected according to specific applications.
Insulation level: Considering safety and reliability, it is necessary to choose an insulation level that meets the application requirements.
Efficiency: High efficiency transformers can reduce energy loss and heat generation, and improve system performance.
6、 Maintenance of high-frequency transformers
In order to ensure the normal operation and prolong the service life of high-frequency transformers, regular maintenance and upkeep are necessary. Here are some key maintenance measures:
Cleaning: Regularly clean the high-frequency transformer, especially the dust and dirt on the surface of the transformer, to ensure good heat dissipation and normal operation.
Check wiring and connections: Regularly inspect the wiring and connection parts of the high-frequency transformer to ensure their tightness and good contact.
Maintaining the cooling system: The cooling system of high-frequency transformers is crucial for their normal operation, and components such as radiators and fans should be regularly cleaned and inspected.
Check insulation condition: Regularly conduct insulation tests to check if the insulation resistance meets the requirements.
Regularly check the load and current: ensure that the high-frequency transformer operates within the specified range to avoid overload and overcurrent problems.
7、 Conclusion
As an important component in electronic devices, high-frequency transformers have a wide range of application prospects in modern electronics industry due to their miniaturization, high efficiency, and low losses. By understanding the principles, structures, characteristics, applications, and maintenance methods of high-frequency transformers, we can better utilize this technology and promote progress and development in related fields.